Review Article | Open
Access
|
Open
Access
|


 | Published online: 22 December 2025
Intrusion Detection in Transition: A Survey of Deep Learning,
Federated Learning, Adversarial, Lightweight, and
Explainable Approaches
| Published online: 22 December 2025
Intrusion Detection in Transition: A Survey of Deep Learning,
Federated Learning, Adversarial, Lightweight, and
Explainable Approaches
Komal M. Dhule* and Rajesh Bansode
Department of Information Technology, Thakur College of Engineering & Technology, Kandivali (East), Maharashtra, 400101, India
*Email: komal.dhule@tcetmumbai.in (K. M. Dhule)
J. Inf. Commun. Technol. Algorithms Syst. Appl., 2025, 1(3), 25314 https://doi.org/10.64189/ict.25314
Received: 27 October 2025; Revised: 17 December 2025; Accepted: 19 December 2025
Abstract
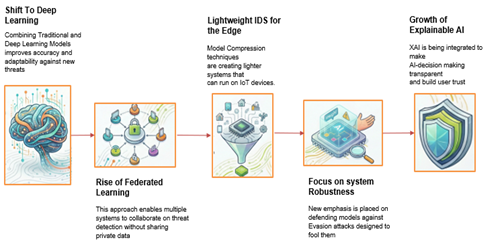
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are still among the central systems in protecting networked settings in contemporary cybersecurity studies. The threats to cyberspace are growing in scale and in severity, and therefore, the challenges to cybersecurity are growing more complex, in a way that necessitates an ongoing evolution of protective systems and the requirement to adjust to the new threats that appear constantly. This review analyzes the new developments in the field of IDS by reviewing new methodological strategies, datasets used for analysis and solution development. It outlines five major trends. To begin with, there is the adoption of less traditional machine-learning approaches in favor of deep-learning models; it is the combination of the paradigms that allows detecting more accurate attacks or improving the ability of the system to follow changing patterns of intrusion. Second, federated learning gains popularity in architectures of IDSs, allowing models to be trained collaboratively while maintaining the privacy of proprietary data. Third, increased attention is paid to the strengthening of the resistance to adversarial perturbations, as evasion methods can easily deceive machine-learning as well as deep-learning models. Fourth, model compression, simplification, and edge-computing methods drive the development of lightweight variants of IDS to run on Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices and various other resource-efficient systems. Fifth, Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) approaches are used to make model behavior interpretable, thus convincing its users to trust these automated systems. Datasets in the survey include CIC-IDS2017, UNSW NB15, and IoT traffic logs, and dwells on problems such as performance evaluation, reproducibility, and benchmarking. These innovations placed in the context of existing challenges provide a holistic description of the evolution of IDS technology and provide important information to researchers as well as industry players. They acknowledge existing weaknesses in the testing procedures and provide a strategic guide on how the research should be conducted in the future to develop more resilient and more reliable next generation intrusion detection architectures.
Graphical Abstract
Novelty statement
This survey presents a holistic analysis of modern intrusion detection systems, identifying emerging challenges and providing future research directions.