Research Article | Open Access
|
Open Access
|


 | Published online: 23 September 2025
Internal Route Optimization in IoT-Enabled Wireless Sensor Networks
Using Cluster-Based Architecture and Adaptive Cluster Head
Communication
| Published online: 23 September 2025
Internal Route Optimization in IoT-Enabled Wireless Sensor Networks
Using Cluster-Based Architecture and Adaptive Cluster Head
Communication
Minal Jain,1,* Khushbu1 and Arun Vaishnav2
1 Faculty of Computer and Application, Madhav University, Abu Road, Pindwara, Rajasthan, 307032, India
2 Faculty of Computing and Informatics, Sir Padampat Singhania University, Udaipur, Rajasthan, 313601, India
*Email: minalshah004@gmail.com (M. Jain)
J. Smart Sens. Comput., 2025, 1(2), 25210 https://doi.org/10.64189/ssc.25210
Received: 22 July 2025; Revised: 12 September 2025; Accepted: 22 September 2025
Abstract
Energy-efficient and intelligent routing strategies have become essential as wireless sensor networks are increasingly incorporated into Internet of Things environments. For IoT-enabled Wireless sensor networks (WSNs), this study suggests an improved internal routing framework with an emphasis on cluster head to sink communication optimization following cluster head selection. Based on a strong cluster formation procedure that employs hybrid fuzzy C-Means and K-Means algorithms, a multi-objective Mother-Inspired Adaptive Optimization method is used to choose the cluster heads. Next, energy- and distance-aware routing paths between cluster heads are dynamically constructed using the Pelican Optimization Algorithm. Key issues in Internet of Things-based deployments, such as limited energy, data latency, and communication reliability, are address by the suggested approach. The results show from prior hybrid optimization- based WSN Studies that the hybrid approach is effective in managing large-scale, resourceconstrained sensor networks within IoT infrastructures by significantly extending network lifetime, improving packet delivery ratio, and lowering end-to-end delay. The results are analyses based on key performance indicators such as routing efficiency, energy consumption, network lifetime, end-to-end delay, and packet delivery ratio. Comparative visualizations illustrate the routing paths optimized by POA, highlighting its effectiveness in minimizing transmission distances and balancing energy usage among Cluster heads (CHs).
Keywords: Wireless sensor networks; Internet of things: Cluster-based routing; Cluster head; Data aggregation; Pelican optimization algorithm; Energy efficiency.
Graphical Abstract
Novelty statement
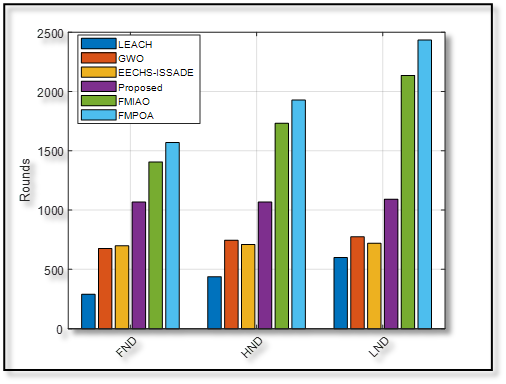
A comparative analysis of three key network lifetime metrics; FND, HND, and LND across various protocols: LEACH, GWO, EECHS-ISSADE, Proposed, FMIAO, and FMPOA.